Applications of Geographic Information System (GIS)
Applications of GIS mostly used in Maps are being used as tools to facilitate decision-making at many different sizes, such as urban planning, and as legal documents that convey jurisdictional borders and land ownership. Large-scale utility networks, such as those that serve water, electricity, and

telecommunications to a multitude of users, can be fully modelled using the GIS. A system like this might function at many levels, simulating service connections to customers, service districts, and intricate facility inventories and layouts, including schematic diagrams and transformer, device, and conduit designs. The following is a list of GIS applications:
Safe navigation on waterways is promoted by web-based navigation maps. For more efficient travel, cargo routes and ferry paths are found. Accurate topography and hydrographic data are provided by ArcGIS, which also supports safe navigation systems. The Coastal Resources Division of the DNR has started using GIS to locate, record, and catalogue these historic wrecks. Through a web map, this section is able to tell
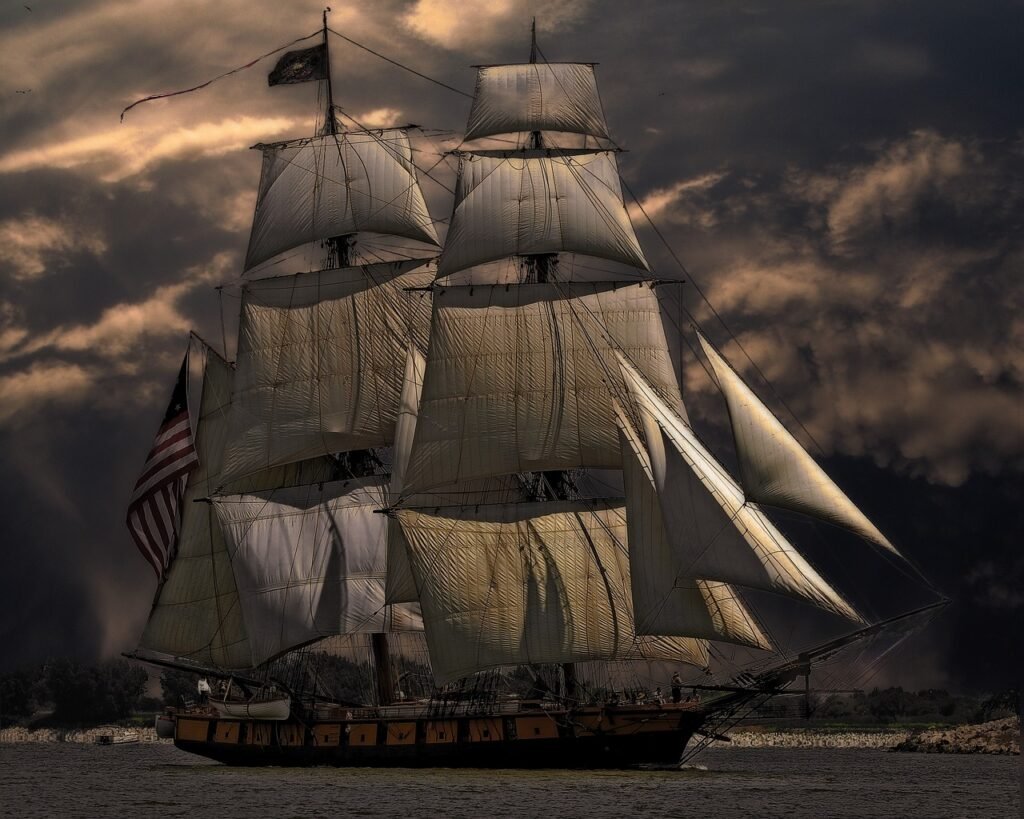

the public about the positions of these vessels. The web map will be updated often to reduce the chance of collisions and injuries among boaters by informing them of these coastal risks.
Application of GIS Surveying:
Measuring an object’s location on the surface of the earth is called surveying. Measuring the angles and separations between various spots on the surface of the earth is called land surveying. GNSS measurements are being used by an increasing number of national, regional, and local governments. For topographic surveys with centimeter-level accuracy, GNSS is utilised. The GIS system may make use of these data. Digital maps can be prepared and area estimates can be made using GIS tools.
Applications of GIS in Geology:

GIS is used by geologists for a variety of purposes. Geological features, soil and stratum analysis, seismic data assessment, and/or three-dimensional (3D) geographic feature creation are all done with the usage of GIS. GIS can also be used to determine the ideal location for a dam by analysing the features of the rock.
Planning and Community Development with GIS:
GIS helps us to address global concerns by providing a deeper understanding of our world. These days, GIS technology is developing quickly, offering an extensive range of new planning innovations and possibilities. By using GIS and proven scientific principles to solve unknown problems, we can improve living quality and pave the way for a brighter future.
We are able to incorporate geographic intelligence into our thoughts and actions through the development and application of GIS technologies and expertise.
Application of GIS for Tourism:

GIS offers a useful toolkit of methods and innovations with a broad range of applications for achieving sustainable tourist development. They will be provided with all the information needed to click, measure distance, locate restaurants and motels, and even go to the relevant links. Information is essential to both the profitability of the tourism business and travellers’ ability to plan their travels. This can benefit travellers as well as the tourism department in numerous ways.
Global Seismic Information System:
An earthquake is one of the most terrifying and damaging natural events that may happen. It is necessary to be aware of the global patterns in earthquake occurrence. The behaviour pattern of earthquakes in the geographical and temporal domain can be better understood by earthquake engineers and seismologists with the aid of a GIS-based user interface system for querying on earthquake catalogues.
Application of GIS Monitoring and Planning for Energy Use:
GIS is a useful technology that supports the organising, planning, and expansion of the utilities and energy sectors. Energy system management is a difficult task that requires skill. Planning, designing, and maintaining facilities can be greatly enhanced with GIS. It also offers better services at a more affordable price.
Studies on Traffic Density:
GIS may be used to handle traffic issues in an efficient manner. The population and amount of traffic on the roads today are growing at an exponential rate. The benefits of GIS make it a desirable solution for dealing with the growing traffic issues. We can create a comprehensive database containing all the traffic data, including speed data, road geometry, traffic flow, and other geographical data, and then process this data to generate a graphical representation of the traffic management situation.
Application of GIS in Space Utilization:
Managers can better organise and see how best to use space by using geographic information systems (GIS). By employing space more effectively, including handling the relocation of personnel and assets as well as the storage supplies, operational expenses can be reduced. Planners can make a virtual walkthrough of the structure and its rooms prior to construction with the use of 3D visualisation found in GIS systems.
Creation of Facilities for Public Infrastructure:
In the area of facility management, GIS is quite beneficial. Facility managers can utilise GIS for emergency and disaster planning and response, space management, visualisation, and planning. It can be applied at every stage of a facility’s life cycle, from space planning to choosing where to develop. It also makes better planning and analysis easier.
Identification of Location:
This method is applied to the process of locating a new retail site. It is useful to ascertain what is present at a specific location. There are numerous methods to describe a place, including by its name, postcode, or geographic reference like longitude, latitude, or X/Y.
Choosing a River Crossing Location for Bridges:
The stability of the slope leading to and up from the river crossing is a crucial geotechnical factor. Gathering historical data on sedimentation and erosion is advised. The amount of river channel contraction, the degree of curvature of the river bend, the kind of bed and bank materials, including the flood flow and the flow depth, can all be accurately and quickly assessed using GIS based on these data. The selection of river crossing locations for bridges has frequently made use of this data.
Application of GIS in Regional Planning:
Planners use Geographic Information System (GIS) technology on a daily basis to do research, create, carry out, and track the development of their plans. Planners, surveyors, and engineers can create and map their cities and neighbourhoods with the help of GIS. Planners employ GIS to speed up the decision-making process. They have the technical know-how, political acumen, and financial comprehension to turn a vision of the future into a strategic action plan for the present. (ESRI, GIS-Based Urban and Regional Planning Solutions)
Town and City Infrastructure:
Integrated planning, construction, and maintenance management databases are connected to center-line drawings for streets, water, and sewer facilities.
Tax Management:
Application of GIS used in Land maps, tax documentation, and assessments for planning and revenue collection.
Services for Emergencies:
addressing unforeseen incidents such as fires, explosions, spills of hazardous materials, and more.
Impacts of an Oil Spill:
For the purpose of tanker spills, war disasters, and real-time emergency operations management, remote sensing and surface-based assessment are utilized.
Wastewater Management:
an integrated planning approach for storm impact planning that includes catch basins, sewers, ditches, and waterways.
Water Quality Management:
Assessing potential outcomes by simulating soil, land use, and watershed features.
Air Emissions:
Risk and dispersion from air toxics in areas near industrial operations are modelled and visualised.
Hazard Analysis:
Conducting hazardous operations analysis for chemical activities involves connecting databases and drawings.
Forestry management:
Application of GIS involves Forestry management using imaging and digital elevation modelling to characterize changes in forest resources and assess the harm that pesticides, fire, logging, and acid rain have caused to forests.
Population Planning:
Distributing people geographically and charting slums and overcrowding in developing nation utilizing images from satellites.
Habit Characterization:
Examining migratory and population trends to help protect threatened and endangered species.
Urban Development Planning:
Predicting real estate growth trends by modelling the dissemination of development processes.
Uses by the Government:
Application of GIS in Monitoring and forecasting changes over time, as well as being able to connect data about resources and activities to a specific area, are essential components of contemporary society. It is impossible to overstate the significance of socioeconomic data in this regard, such as that which is generated by national censuses. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are used by international, national, regional, and local governments for a wide range of purposes. These include risk avoidance and environmental management through urban and rural policy decisions, defense and law enforcement through regional planning, and daily operational tasks like land registration, property taxation, and traffic routing.
Uses in Industry and Commerce:
There are numerous ways that industry and commerce employ GIS. Utility (power, gas, water, and telephone) corporations are significant users of digital geographic information systems (GIS) technology for supply network management and monitoring, frequently across international borders.
For business objectives:
companies utilize GIS in conjunction with other economic data to identify the best routes for deliveries, possible markets, and locations for stores and factories. GI is used by builders of major infrastructure, such as roads, trains, and bridges, to calculate the quantities and costs of the materials required.
Agricultural purposes:
GIS is used to evaluate yields and management techniques in industries like forestry, mining, agriculture, and water resources.
Consultants in the service sector use GIS to offer suggestions on how to boost company productivity or to offer transport and tourism services.
Social purposes:
GIS is used in social investigations to assist in the analysis of population characteristics that vary geographically, such as income, crime, health, or housing quality.
Environmental uses:
From erosion, flooding, and soil, air, and water pollution to global warming and sea level rise, GIS is employed in a wide range of real-world environmental challenges.





good
Thank you