Remote sensing technology has revolutionized our ability to observe and understand the Earth’s surface from a distance. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of remote sensing, its applications, and its significance in various fields.
1. Introduction to Remote Sensing
Remote sensing is the process of gathering information about objects or areas from a distance, typically through sensors mounted on satellites, aircraft, or drones. It allows us to collect data without direct contact with the subject, enabling comprehensive observations over large areas.
2. History and Evolution of Remote Sensing Technology
Remote sensing traces its roots back to aerial photography in the 19th century. However, the modern era of remote sensing began with the launch of satellites in the 20th century, such as Landsat and NOAA, which provided high-resolution images of the Earth’s surface.
3. Principles of Remote Sensing
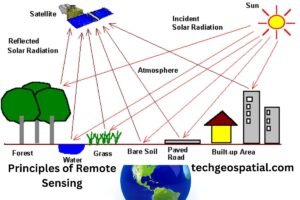
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Remote sensing operates on the principle of capturing electromagnetic radiation reflected or emitted by objects on Earth. Different wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum provide unique information about the properties of the observed objects.
Remote Sensing Platforms
Remote sensing platforms include satellites, aircraft, drones, and ground-based sensors. Each platform offers distinct advantages in terms of coverage, resolution, and cost, catering to diverse remote sensing needs.
4. Types of Remote Sensing
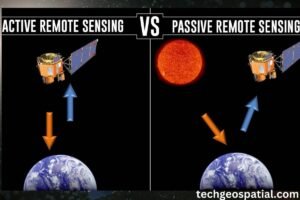
Active Remote Sensing
Active remote sensing involves emitting energy, such as radar or lidar, and measuring the reflected or scattered signals. This technique is particularly useful for penetrating clouds and vegetation, making it ideal for mapping terrain and monitoring changes.
Passive Remote Sensing
Passive remote sensing relies on natural sources of radiation, such as sunlight, to illuminate objects. Sensors detect the reflected or emitted radiation, providing valuable data on surface properties, vegetation health, and atmospheric conditions.
5. Applications of Remote Sensing
Remote sensing finds applications across various sectors, including:
Agriculture
Remote sensing aids farmers in monitoring crop health, assessing soil moisture levels, and optimizing irrigation practices. It enables precision agriculture, leading to improved crop yields and resource efficiency.
Environmental Monitoring
Remote sensing plays a crucial role in monitoring environmental changes, such as deforestation, land degradation, and habitat loss. It provides valuable insights for conservation efforts and sustainable land management.
Urban Planning
Remote sensing supports urban planners in analyzing land use patterns, monitoring urban expansion, and assessing infrastructure development. It facilitates informed decision-making for sustainable urban growth and resilience.
Disaster Management
Remote sensing assists in disaster preparedness, response, and recovery efforts by providing timely information on natural hazards, such as floods, wildfires, and earthquakes. It helps authorities assess damage, plan evacuation routes, and prioritize relief efforts.
6. Advantages of Remote Sensing
Remote sensing offers several advantages, including:
- Wide area coverage
- Cost-effectiveness
- Non-invasive data collection
- Multispectral and temporal analysis
- Accessibility to remote or hazardous areas
7. Challenges and Limitations
Despite its benefits, remote sensing faces challenges such as:
- Atmospheric interference
- Cloud cover
- Data processing complexities
- Limited spatial and spectral resolution
- Legal and ethical considerations regarding privacy and data sharing
8. Future Trends in Remote Sensing
The future of remote sensing holds promising developments, including:
- Advancements in sensor technology
- Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning
- Expansion of microsatellite constellations
- Enhanced data fusion and interoperability
- Continued collaboration for global data sharing and standardization
9. Conclusion
Remote sensing technology continues to redefine our understanding of the Earth’s surface and its dynamic processes. From agriculture to disaster management, its applications are vast and diverse, driving innovation and sustainable development worldwide.
FAQs
-
How does remote sensing benefit agriculture? Remote sensing helps farmers monitor crop health, assess soil moisture, and optimize resource allocation, leading to increased productivity and sustainability.
-
What are the limitations of remote sensing technology? Challenges include atmospheric interference, cloud cover, data processing complexities, and legal/ethical considerations regarding data usage.
-
What role does remote sensing play in environmental monitoring? Remote sensing provides valuable data for monitoring deforestation, land degradation, habitat loss, and other environmental changes, supporting conservation efforts.
-
How is remote sensing used in disaster management? Remote sensing aids in disaster preparedness, response, and recovery by providing timely information on natural hazards, enabling effective planning and resource allocation.
-
What are the future trends in remote sensing technology? Future developments include advancements in sensor technology, integration of AI/ML, expansion of satellite constellations, and enhanced data fusion for improved analysis.